Are you an e-bike enthusiast or considering joining the electric bike revolution? If so, you’ve likely encountered the maze of e-bike regulations that vary dramatically from state to state. In this article, we delve into the current e-bike regulation chaos, shedding light on the disparities that can leave riders, retailers, and manufacturers bewildered.
Join us as we explore the need for more uniform e-bike laws and the role manufacturers and retailers play in creating a safer and more regulated e-bike landscape. Whether you’re a seasoned e-bike rider or a newcomer to this eco-friendly mode of transportation, understanding the evolving world of e-bike regulations is essential.
The Current E-Bike Regulation Chaos

Did you know that e-bike-related accidents are on the rise? With e-bikes capable of reaching speeds up to 28 mph, they’ve outpaced traditional bicycles, raising concerns about rider safety and control.
If you own or are planning to buy an e-bike, you might be surprised to learn that the laws regulating them vary greatly from state to state. This lack of uniformity can be confusing and frustrating for riders, retailers, and manufacturers alike.
At the federal level, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has the authority to impose penalties of up to $24,000 per noncompliant motorcycle, to a maximum penalty of $122.1 million. Both the NHTSA and the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) can also impose mandatory recalls of non-compliant products. A bike that’s not really a bike or an electric motorcycle that doesn’t meet electric motorcycle requirements could trigger the penalties.
In April 2020, the Department of the Interior proposed new rules regulating the use of electric bikes (e-bikes) on public lands. E-bikes are motor-assisted bicycles controlled with a handlebar throttle or activated through pedaling. E-bikes’ ambiguous position between traditional bicycles and motorcycles has led to controversy over whether e-bikes should be permitted on non-motorized trails.
At the state level, the laws regulating e-bikes vary widely. For example, in New York, e-bikes are only legal if they have a maximum speed of 20 mph and a motor no more powerful than 750 watts. In California, e-bikes are classified into three categories: Class 1, 2, and 3, each with its own set of regulations. In Michigan, e-bikes are classified as bicycles as long as they have a motor with a maximum power output of 750 watts and a top speed of 20 mph. In Oregon, e-bikes are classified into four categories, and each has its own set of regulations.
This lack of uniformity in e-bike regulations can create confusion for riders who may unknowingly break the law by riding in a state where their e-bike is not legal. It can also create headaches for retailers and manufacturers who must navigate a patchwork of regulations when selling and distributing e-bikes across the country.
To address this issue, some states have taken steps to create more uniform e-bike regulations. For example, Tennessee passed a law in 2018 that created a uniform set of regulations for e-bikes across the state. Washington, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Minnesota, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Alabama, Massachusetts, New Mexico, and Wyoming still have varying e-bike regulations and laws.
In conclusion, the current state of e-bike regulation in the United States is chaotic and confusing, with regulations varying widely from state to state. This lack of uniformity can create problems for riders, retailers, and manufacturers, and highlights the need for more unified e-bike laws across the country.
Understanding E-Bikes and Their Uses

You may have heard of e-bikes, electric bikes, or electric bicycles, but do you know what they are and how they work? E-bikes are bicycles with an electric motor that assists the rider’s pedaling. They are becoming increasingly popular as a form of transportation due to their convenience and eco-friendliness.
E-bikes come in different classes, each with specific regulations and speed limits. Class 1 e-bikes are pedal-assist only, with no throttle, and have a maximum assisted speed of 20 mph. Class 2 e-bikes also have a maximum speed of 20 mph, but are throttle-assisted. Class 3 e-bikes are pedal-assist only, with no throttle, and a maximum assisted speed of 28 mph. It is important to understand the class of your e-bike to ensure you are following the correct regulations.
E-bikes can be used for various purposes, including transportation, recreation, and exercise. They are a great alternative to traditional bicycles, as they allow riders to travel further and faster with less effort. E-bikes can also be used to replace mopeds or scooters for short commutes. They are a cost-effective and environmentally friendly mode of transportation, as they do not require gas and emit fewer pollutants than cars.
It is important to note that e-bikes are not the same as traditional bicycles. While they share many similarities, e-bikes have an electric motor that assists the rider’s pedaling. This means that e-bikes can travel faster and further than traditional bikes with less effort. However, e-bikes are still subject to many of the same regulations as traditional bikes, such as helmet laws and traffic laws.
In conclusion, e-bikes are a growing trend in transportation due to their convenience and eco-friendliness. They come in different classes with specific regulations and speed limits. E-bikes can be used for various purposes, including transportation, recreation, and exercise. It is important to understand the differences between e-bikes and traditional bikes and follow the correct regulations to ensure a safe and enjoyable ride.
Safety Concerns and E-Bikes

E-bikes are a convenient and eco-friendly way to get around, but they also pose safety concerns. With the increasing popularity of e-bikes, the number of accidents involving them is also on the rise. According to Fortune, cities must do more to regulate e-bikes, such as banning them from dirt trails and better educating riders about safety.
One of the main safety concerns with e-bikes is their speed. E-bikes can reach speeds of up to 28 mph, which is faster than most traditional bicycles. This increased speed can make it difficult for riders to control their bikes, especially when navigating through traffic. Additionally, e-bikes are heavier than traditional bicycles, which can make them more difficult to maneuver and stop in emergency situations.
Another safety concern with e-bikes is the risk of hazardous materials. E-bike batteries contain lithium-ion, which can be dangerous if not handled properly. According to the National Fire Protection Association, e-bike and e-scooter battery fires have been associated with faulty charging equipment, improper charging practices, and overloaded electrical circuits.
To address these safety concerns, there are safety requirements that e-bikes must meet. For example, e-bikes must have working brakes, lights, and reflectors. In addition, e-bikes must meet certain speed limits and weight restrictions. However, these safety requirements vary from state to state, which can create confusion and lead to inconsistent enforcement.
Overall, while e-bikes offer many benefits, it is important to be aware of the safety concerns associated with them. By following safety requirements and regulations, you can help ensure a safe and enjoyable ride.
The Role of Manufacturers and Retailers

As a manufacturer or retailer of e-bikes, you play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of this eco-friendly mode of transportation. Your actions can have a significant impact on the industry’s growth and the public’s perception of e-bikes. Here are some ways in which you can contribute to the development of a unified regulatory framework for e-bikes:
Manufacturers
As a manufacturer, you can help by:
1) Providing clear and accurate information about your e-bike models, including their classification, speed, and power output. This information can help consumers make informed decisions and avoid purchasing an e-bike that is not legal in their jurisdiction.
2) Collaborating with industry associations and government agencies to develop common standards and guidelines for e-bikes. This can help reduce confusion and ensure that e-bikes are regulated consistently across different regions.
3) Investing in research and development to improve the safety and performance of e-bikes. This can help address some of the concerns that regulators and the public have about e-bikes, such as their speed and handling characteristics.
4) Educating your customers about the proper use and maintenance of e-bikes. This can help reduce the risk of accidents and ensure that e-bikes remain a safe and reliable mode of transportation.
Retailers
As a retailer, you can help by:
1) Ensuring that your e-bikes are properly classified and labeled according to local regulations. This can help avoid confusion and prevent customers from purchasing an e-bike that is not legal in their jurisdiction.
2) Providing customers with accurate information about the laws and regulations that apply to e-bikes in their area. This can help customers make informed decisions and avoid getting into legal trouble.
3) Offering training and education programs for customers who are new to e-bikes. This can help ensure that customers are comfortable and confident when riding their e-bikes and reduce the risk of accidents.
4) Advocating for clear and consistent regulations for e-bikes. This can help create a level playing field for e-bike manufacturers and retailers and ensure that e-bikes are regulated in a way that promotes safety and innovation.
By working together, manufacturers and retailers can help create a more coherent and effective regulatory framework for e-bikes. This can help promote the growth of the e-bike industry and ensure that e-bikes remain a safe and sustainable mode of transportation for years to come.
The Need for Unified Laws

If you’re an e-bike rider or considering getting one, you might have noticed that e-bike laws and regulations vary widely from state to state and even from city to city. This can create a lot of confusion and frustration, not to mention safety concerns. That’s why there is a growing need for unified e-bike laws across the country.
Currently, e-bike regulations cover a wide range of topics, including speed limits, power limits, where you can ride, and helmet requirements. These regulations are set by different entities, such as states, cities, and even federal agencies. This patchwork of regulations can make it difficult to know what rules you need to follow, especially if you’re traveling to a new area.
Unified e-bike laws would not only make it easier for riders to know what the rules are, but they could also help to increase safety on the roads. For example, if every state had the same speed limit for e-bikes, it would be easier for drivers to know how fast they can expect e-bikes to be going. This could help to reduce accidents and make the roads safer for everyone.
In addition to safety, unified e-bike laws could also help to reduce confusion and increase access to e-bikes. If the laws were the same across the country, it would be easier for e-bike manufacturers to produce bikes that meet the requirements. This could lead to more affordable and accessible e-bikes for everyone.
Of course, creating unified e-bike laws is easier said than done. It would require cooperation between federal, state, and local governments, as well as input from e-bike riders and manufacturers. However, the benefits of unified e-bike laws are clear, and it’s something that should be pursued in order to make e-biking safer and more accessible for everyone.
E-Bike Regulations in Different States
Navigating the world of e-bike regulations can be confusing, especially with different laws in different states. Some states have adopted the three-class system, while others have their own unique laws. Here’s a breakdown of e-bike regulations in different states:
- Arizona: Class 1 and Class 2 e-bikes are allowed on bike paths and multi-use paths, while Class 3 e-bikes are not allowed on these paths.
- Arkansas: E-bikes are classified as bicycles and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Colorado: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are allowed on bike paths and multi-use paths unless otherwise posted.
- Connecticut: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Delaware: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Florida: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Georgia: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Hawaii: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Idaho: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Illinois: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Indiana: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Iowa: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Kansas: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Kentucky: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Louisiana: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Maine: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Maryland: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Massachusetts: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Minnesota: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Mississippi: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Montana: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Nebraska: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Nevada: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- New Hampshire: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- New Jersey: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- New Mexico: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- New York: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- North Carolina: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Ohio: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Oklahoma: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Pennsylvania: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Rhode Island: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- South Carolina: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- South Dakota: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Texas: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Utah: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Vermont: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Virginia: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Washington: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- West Virginia: E-bikes are classified into three categories and are subject to the same laws as bicycles.
- Wisconsin: Wisconsin classifies electric bicycles into three categories based on motor assistance, with no motor vehicle registration or insurance requirements.
- Wyoming: Wyoming regulates e-bikes like regular bicycles, exempting them from motor vehicle requirements. Three classes of e-bikes exist based on capabilities.
Unified e-bike laws would not only make it easier for riders to know what the rules are, but they could also help to increase safety on the roads. This could help to reduce accidents and make the roads safer for everyone.
The Three-Tiered E-Bike Classification System
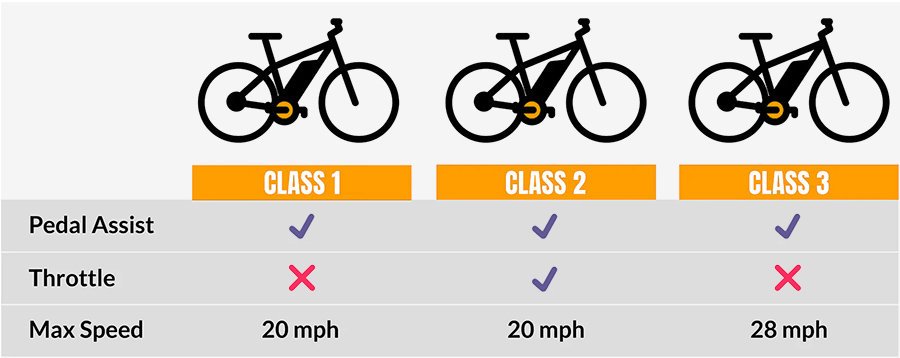
Knowing the classification system can help you choose the right e-bike for your needs and ensure that you’re complying with the regulations in your state.
If you’re looking to buy an e-bike, it’s essential to know the different types available. The three-tiered e-bike classification system helps you understand the capabilities of each type of e-bike. This system classifies e-bikes into three categories: Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3.
Class 1
Class 1 e-bikes are pedal-assist bikes with a maximum speed of 20 mph. They have a motor that assists the rider when pedaling, but the motor stops providing assistance once the bike reaches 20 mph. Class 1 e-bikes are allowed on bike paths and bike lanes.
Class 2
Class 2 e-bikes are also known as throttle-assist bikes. They have a motor that can be activated by a throttle, which propels the bike forward without pedaling. Class 2 e-bikes also have a maximum speed of 20 mph. They are allowed on bike paths and bike lanes.
Class 3
Class 3 e-bikes are pedal-assist bikes with a maximum speed of 28 mph. They have a motor that assists the rider when pedaling, but the motor stops providing assistance once the bike reaches 28 mph. Class 3 e-bikes are not allowed on bike paths, but they are allowed on bike lanes and roads.
It’s important to note that the three-tiered e-bike classification system is not universal. Some states have their own regulations, and some states don’t have any regulations at all. Before purchasing an e-bike, it’s important to research the regulations in your state to ensure that you’re complying with the law.
In conclusion, the three-piece d e-bike classification system is a useful tool for understanding the speed capabilities of different types of e-bikes. Knowing the classification system can help you choose the right e-bike for your needs and ensure that you’re complying with the regulations in your state.
E-Bike Regulations in Europe and North America
If you’re planning to ride an e-bike in Europe or North America, it’s important to understand the regulations surrounding these vehicles. E-bike regulations can vary significantly between countries and even cities, leading to confusion and uncertainty for riders.
In Europe, e-bike regulations are generally more standardized than in North America. The European Union has established regulations for e-bikes that cover everything from motor power to speed limits. For example, e-bikes in Europe are typically limited to a maximum motor power of 250 watts and a top speed of 25 km/h.
In North America, e-bike regulations can vary significantly between states and cities. For example, in California, e-bikes are classified into three categories based on motor power and speed. Class 1 e-bikes have a maximum motor power of 750 watts and a top speed of 20 mph, while Class 2 e-bikes have a maximum speed of 28 mph and a throttle. Class 3 e-bikes have a maximum speed of 28 mph but require pedaling to activate the motor.
In Canada, e-bike regulations are set at the provincial level. For example, in Ontario, e-bikes are limited to a maximum motor power of 500 watts and a top speed of 32 km/h. In Quebec, e-bikes are limited to a maximum motor power of 1,000 watts and a top speed of 32 km/h.
In London, e-bike regulations are similar to those in the rest of the UK. E-bikes are limited to a maximum motor power of 250 watts and a top speed of 25 km/h. However, there are plans to introduce new regulations that would allow e-bikes with a motor power of up to 500 watts on the roads.
It’s important to note that e-bike regulations can change over time, so it’s important to stay up-to-date with the latest rules and regulations in your area. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to wear a helmet and follow the rules of the road when riding an e-bike.
Conclusion: The Way Forward for E-Bike Regulations
With the increasing popularity of e-bikes, it is essential to have unified laws and regulations that are accessible and easy to understand for everyone. The current chaos surrounding e-bike regulation is not only confusing but also dangerous for riders and pedestrians alike.
To move forward, it is crucial to establish clear guidelines for e-bike use on public roads, bike lanes, and backcountry trails. This will ensure the safety of all users and prevent any potential conflicts. Peopleforbikes is a great resource for information on e-bike laws and regulations, and we recommend checking out their website for more information.
It is also important to consider the accessibility of e-bikes for seniors and people with limited mobility. The proposed rules expanding e-bike access to increase recreation opportunities and accessibility of public lands to seniors and others with limited mobility are a step in the right direction. However, it is crucial to ensure that these rules are implemented in a way that does not harm the environment or other trail users.
In conclusion, e-bike regulation chaos can be resolved with unified laws and regulations that prioritize the safety of all users while also considering accessibility and environmental impact. We urge lawmakers and e-bike enthusiasts to work together to establish clear guidelines and regulations that benefit everyone.

